Sustainable Blister Packaging is very important today, as the pharmaceutical industry is packing billions of medicinal products in non-recyclable blister packs every year.
More than 70% of prescription medicines have been packed in blisters which are the combination of plastic and aluminum foil.
Unfortunately, this combination is nearly impossible to separate and recycle which increases waste or plastic pollution.
The growing pollution caused by these non-recyclable blister packs is the main reason for adopting sustainable blister packaging in the pharmaceutical industry.
Here, we will talk about sustainable blister packaging. We will cover the different types of blister packs, a list of traditional materials used, and available sustainable materials and methods.
Introduction
What is Blister Packaging?
Blister packaging is a type of packaging where a product is sealed in a clear plastic pocket with the help of aluminum or paper foil.
It is widely used to pack products that require protection and visibility, like medicine, consumer goods, toys, or small electronics.
For example, when you buy medicine from a pharmacy store, you may notice that each tablet or capsule is trapped in its own small plastic pocket. This is called blister packaging!
It is a very simple and cost-effective method to protect products while allowing consumers to see what they are buying.
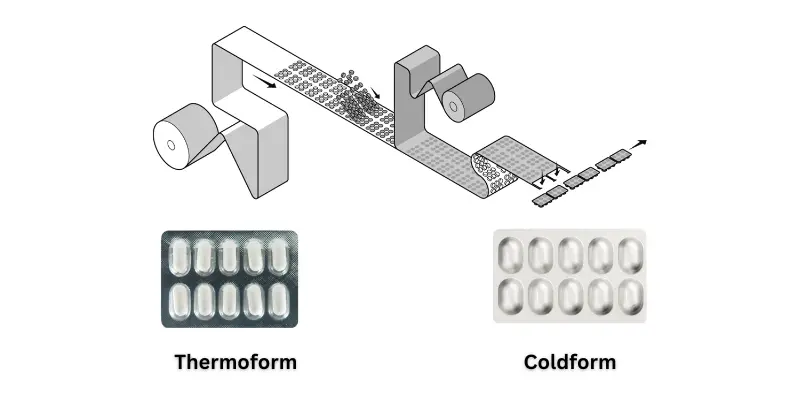
Types of Blister Packaging
Thermoforming and cold forming are the two main methods used in pharmaceutical blister packaging. Let’s understand it step by step.
1. Thermoforming Blister Packaging
Thermoforming is the most widely used method for producing blister packs, especially in the pharmaceutical and consumer goods industry. Let’s break down the thermoforming process in a few steps.
1. Heating and Softening: The PVC (Polyvinyl Chloride) sheet is heated to make it soft and pliable. This step is necessary to form blister pockets.
2. Creating the Cavity: Once the PVC material is soft, vacuum pressure is applied to pull the material into the mold cavity to form a blister pocket that is perfectly fit for the product.
3. Cooling and Filling: After the cavity formation, the PVC material is cooled to solidify. The product is then fed into each blister cavity.
4. Sealing the Pack: Finally, the blister is sealed with aluminum or paper foil to create a final pack.
Thermoforming blister packaging is commonly used because of its cost, flexibility, visibility, and protective qualities.
2. Cold Form Blister Packaging
Cold-form blister packaging works differently from thermoforming because it doesn’t require heat to form a blister pocket. Let’s know how it works.
1. Punched Material Web: Instead of heating the plastic sheet, the cold forming technique directly uses a plug to form a blister pocket. It doesn’t require heat, so it is called cold-form blister pack.
2. Forming the Pocket: The cold form film is placed on the mold cavity and pressed by the plug to form the blister cavity. This method is very useful to pack thermolabile products which are very sensitive to heat.
3. Filling and Sealing: After the pocket formation, the product is filled into each cavity and then sealed with aluminum or paper foil. Cold-form blister pack offers the best protection against moisture, gas, and light. It is widely used in pharmaceutical to pack sensitive products, like Antibiotics, Hormones, Vitamins, and Supplements.
Traditional Materials Used in Blister Packaging
Blister packaging can be done using different materials, such as PVC, PVC/PVdC, Aclar, Cold-form film, aluminum foil and paper film. These materials are selected based on product characteristics, especially in the pharma, food and cosmetic industries.
Look at the most commonly used materials in blister pack.
1. PVC (Polyvinyl Chloride)
PVC is a very popular choice for thermoformed blister packaging. It is a cost-effective and flexible plastic material that offers excellent clarity and functionality.
2. PVC/PVdC (Polyvinyl Chloride/Polyvinylidene Chloride)
This material is a combination of PVC and PVdC. PVdC is coated onto the PVC film to improve its barrier properties against moisture and gas. It is used when a product needs extra protection from external factors.
Like PVC, this material also offers good clarity along with barrier properties.
How to Distinguishing Between PVC and PVC/PVdC?
Although PVC (Polyvinyl Chloride) and PVC/PVdC (Polyvinyl Chloride/Polyvinylidene Chloride) may appear visually the same, they can be differentiated through a simple physical test. By repeatedly striking a plastic sheet against a hard surface.
PVC/PVdC: This material will exhibit a milky white line along the area of impact.
PVC: This material will tend to break apart into pieces more easily.
This test provides an effective means of identifying the difference between PVC and PVC/PVdC.
3. Aclar
Aclar is known for its excellent barrier properties and is often used to pack sensitive medicine that requires the highest protection.
However, it is less likely to be used in packaging because of cost and availability factors.
Aclar is owned by Honeywell International Inc., a multinational conglomerate that manufactures a wide range of products, including materials for the packaging industry.
4. Cold Form Film (25OPA/45AL/60PVC)
The cold-form film is a complex laminate of oriented polyamide (25µ), aluminum (45µ) and PVC (60µ). Because of aluminum in laminate structure, it provides excellent barrier properties against moisture, oxygen and light.
It has a very low WVRT (Water Vapor Transmission Rate) and OTR (Oxygen Transmission Rate), providing the best protection for sensitive molecules.
5. Aluminum Foil (20 and 25 Micron)
Aluminum foil is widely used in blister packaging, especially in pharmaceutical products that require extra protection from environmental factors. The foil is used as a lidding material in both thermoformed and cold-formed blister packs.
As a non-permeable material and inert metal, it is the first line choice for pharmaceutical industry.
6. Paper Film
Paper film is a combination of paper and polyethylene, polyethylene is generally used as a sealant layer for paper film. Paper material is less frequently used in pharmaceuticals due to its lesser barrier properties compared to other materials.
However, when it comes to sustainability, paper film is an excellent choice because of its compostable and recyclable nature.
Traditional materials provide enough protection and visibility, but their frequent use creates huge plastic pollution due to their non-recyclable nature. Moreover, some plastic materials have a negative impact on the environment.
Negative Impact of Traditional Blister Packaging
Here, we will talk about PVC (Polyvinyl Chloride) since it is the most widely used plastic material having a halogenated compound.
During production, use, and disposal, PVC releases toxic chemicals like dioxins, which are harmful to both the environment and human health.
1. Waste Accumulation in Landfills
PVC is non-biodegradable, so it can persist in landfills for hundreds of years. PVC is often combined with other lidding materials, like aluminum foil or paper film, which makes them nearly impossible to separate for recycling.
As a result, large amounts of PVC blister packs accumulate in landfills and create huge plastic pollution over time. Even more by staying in landfills, PVC material reduces soil fertility.
2. Ocean Pollution
Improperly discarded PVC blister packs finally reach to the ocean, where it is fragmented into harmful microplastic due to exposure to saline water and direct sunlight.
These particles are very dangerous for marine creatures and eventually can enter into the human food chain through seafood consumption.
3. Release of Toxic Chemicals
PVC plastic materials release toxic chemicals, such as dioxins, phthalates and other additives on disposal.
These chemicals contaminate our ground water which can’t be filtered out by our water purifier. These toxic chemicals are well-known for serious health problems, like cancer, hormonal imbalances and reproductive issues.
4. Energy-Intensive Production
The manufacturing of PVC plastic material requires a substantial amount of energy, resulting in high carbon emissions.
This makes PVC production less sustainable compared to other materials like PET, PP and HDPE, which have lower carbon footprints.
5. Toxic Fumes When Incinerated
Heating PVC film during packaging generates dioxin gases, which can pose serious health risks to machine operators.
Additionally, when PVC is burned as waste, it produces hydrochloric acid (HCl) and other corrosive substances, which can contaminate soil and reduce its fertility.
Moving away from PVC blister packs to other sustainable blister packs is very important today to protect the environment for future generations.
Sustainable Techniques in Blister Packaging
With the growing trend of sustainability in every sector, the pharmaceutical industry is also exploring sustainable techniques and packaging materials to reduce waste and promote a circular economy.
Below are a few sustainable techniques that can be implemented.
1. Use of Biodegradable and Compostable Materials
Biodegradable and compostable materials are made from natural resources like plants or organic materials that break down naturally and reduce long-term waste.
These materials offer a more sustainable option compared to other plastic materials, which can persist in landfills for hundreds of years.
By choosing biodegradable and compostable materials for blister packaging, manufacturers can support eco-friendly practices and reduce their environmental footprint.
2. Use of Recycled Materials
The use of recycled material in blister packaging is one of the most effective way to reduce the environmental impact of pharmaceutical packaging.
r-PET (Recycled Polyethylene Terephthalate), r-PP (Recycled Polypropylene), and r-HDPE (Recycled High-Density Polyethylene) are increasingly being used as sustainable alternatives to traditional PVC materials.
These materials not only help to reduce plastic waste but also support the circular economy by giving new life to products made from post-consumer plastic.
r-PET (Recycled PET) is made from recycled PET bottles, such as water bottles. PET has a high recycling rate and can be reused in a variety of products, including blister packaging. By using r-PET, we can reduce the need for virgin material and carbon emission.
r-PP (Recycled Polypropylene) is made from post-consumer polypropylene products, like food containers. Polypropylene is easy to recycle in comparison with PVC. By using recycled polypropylene, we can reduce the amount of plastic waste in landfills or oceans.
r-HDPE (Recycled HDPE) is another common material used in sustainable packaging. Like r-PET and r-PP, r-HDPE is made from recycled plastic, often from items like milk jugs or detergent bottles. Recycled HDPE can be reused in blister packs while maintaining strength, durability, and recyclability.
Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET), Polypropylene (PP) and High-density polyethylene (HDPE) are considered much safer and more sustainable alternatives in comparison with PVC material.
Related Post: What is PCR Plastic Packaging.
3. Minimum Use of Material
By optimizing the design and thickness of materials, we can cut down waste generation and reduce energy consumption during material production. This is the best way to make your pack sustainable.
This technique is not only conserving natural resources but also reducing the production costs and carbon footprint of packaging.
4. Energy-Efficient Machinery
Using energy-efficient machinery in the manufacturing process reduces the overall carbon footprint of blister packaging.
AI-driven machines consume less energy and generate less waste during machine setup and the packaging process.
This green shift towards energy-efficient production helps to reduce operating costs and contributes to the global effort to reduce greenhouse gas emissions, supporting a more sustainable manufacturing process.

5. Sustainable Ink and Printing Techniques
In traditional printing and packaging, solvent-based inks are used, which are harmful to the environment. However, sustainable inks, such as water-based or soy-based inks are now available for sustainable printing and packaging.
These inks have a lower environmental impact and do not leave toxic residue on disposal.
By using sustainable ink and printing methods, manufacturers can significantly reduce the environmental footprint of the printing, while still providing high-quality designs and labeling.
These techniques show how the packaging industry can innovate to reduce waste, conserve resources, and lower carbon emissions while still providing protection and visibility for products.
Sustainable Materials for Blister Packaging
Apart from sustainable techniques, adopting eco-friendly materials are equally important for sustainable blister packaging. Let’s look at the few sustainable materials available in the market for blister packaging.
1. Paper Blister Pack
Paper blister packs are an innovative, sustainable option to traditional plastic-based blister packs.
Made primarily from paper and fiber-based materials, paper blister packs offer an eco-friendly solution that eliminates the need for plastics.
These packs can be used in various industries, including pharmaceuticals, cosmetics, and consumer goods.
Practical Example
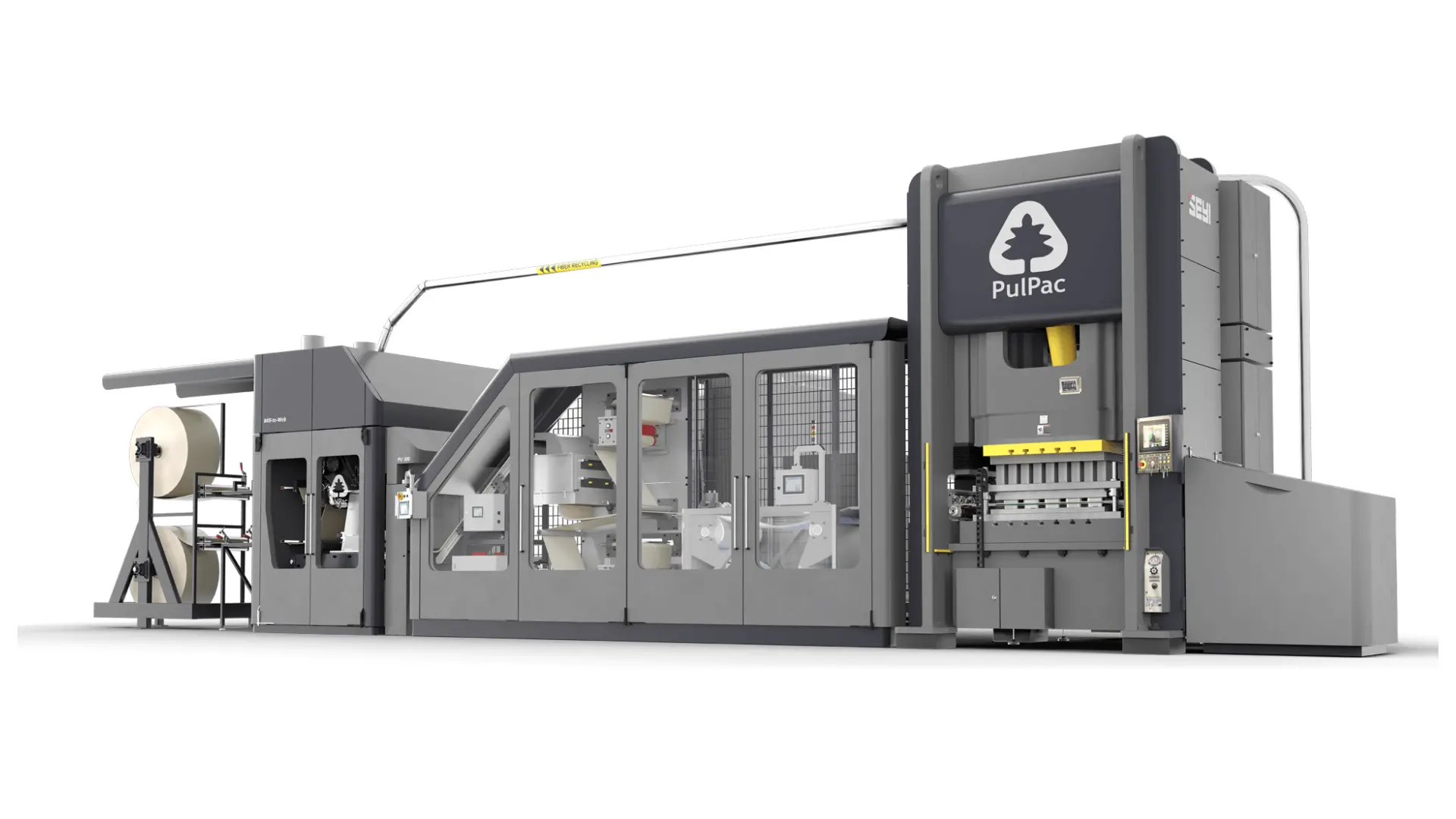
A great example of paper blister packaging is the Collective Blister Pack, developed by PULPAC in collaboration with PA Consulting.
By using a patented process called Dry Molded Fiber Technology, Pulpac produces a sturdy and compostable paper blister pack that can replace plastics completely in the future.
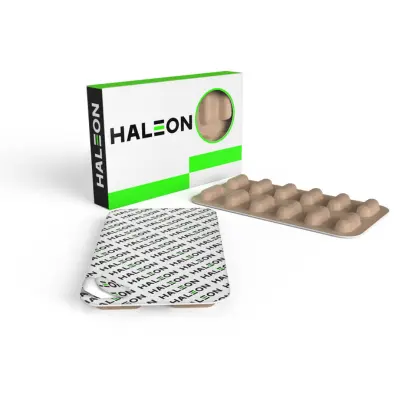
The collective blister pack has been adopted by major pharmaceutical and consumer giants like Bayer, Haleon, and Sanofi for packaging their products.

2. PET Mono-Material Blister Pack
Mono-material blister pack using PET material is the best way to pack pharmaceutical products, which simplifies the recycling process while providing enough protection and excellent clarity.
In this blister pack, the lidding and base materials are made from the same material.
This innovation helps to replace the traditional PVC blister packs, which are typically made from a combination of plastic and aluminum that are difficult to separate and recycle.
Practical Example
Huhtamaki’s Push Tab® Blister Lid and Klöckner Pentaplast‘s kpNext™ R1 Base Film are classic examples of sustainable blister packaging.
Additionally, it runs on existing blister packaging machines without modifications.
This collaboration between Huhtamaki and Klöckner Pentaplast offers a plug-and-play solution for sustainable blister packaging.

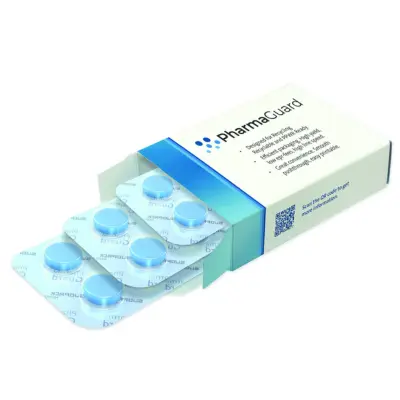
3. PP Mono-Material Blister Pack
Similar to PET mono-material blister packs, PP mono-material blister packs also become a sustainable choice for blister packaging, which is made from propylene gas.
These packs offer an eco-friendly solution that eliminates complex laminate of plastic and aluminum, like PVC blister packs while simplifying recycling and reducing environmental impact.
Ideal for the pharmaceutical and consumer goods industries, PP mono-material blister packs provide excellent product protection, visibility, and tamper-evidence, while supporting the shift towards more sustainable packaging options.
Practical Example
SÜDPACK has developed the PharmaGuard, a mono-material PP blister pack to simplify recycling and reduce environmental impact.
This blister pack is perfect for the pharmaceutical industry, which provides a strong seal, clear visibility, excellent protection and compatibility with existing machinery.
SÜDPACK’s PP mono-material blister pack significantly reduces CO₂ emissions and conserves water and energy during production, making it a more sustainable packaging option compared to traditional materials like PVC and aluminum.
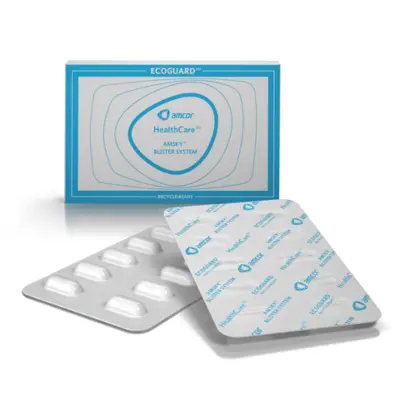
4. HDPE Mono-Material Blister Pack
HDPE mono-material blister packs are an innovative, eco-friendly solution that uses High-Density Polyethylene (HDPE) as the same material for both the lidding and base film.
This type of blister pack eliminates the need for multi-material packaging, making recycling easier and reducing the environmental impact.
HDPE is widely recognized for its strength, durability, and recyclability, making it an ideal choice for creating sustainable packaging in industries like pharmaceuticals, food, and consumer goods.
Practical Example
Amcor, a global leader in packaging solutions, has developed the Amsky HDPE mono-material blister pack, offering a sustainable alternative to traditional PVC blister packs.
This solution is made entirely from HDPE, ensuring recyclability and a more environmentally friendly packaging process.
The Amsky blister pack maintains the same high-performance qualities as conventional blister packs, with strong barrier protection for sensitive products, making it ideal for pharmaceutical and consumer applications.
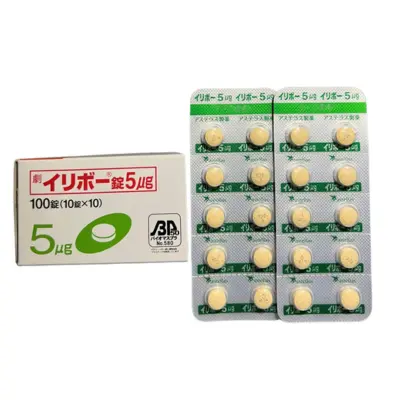
5. Bio-Blister Pack
Bio-blister packs are made from polyethylene derived from renewable resources like sugarcane.
By using plant-based materials, bio-blister packs reduce reliance on fossil fuels and help to reduce carbon emissions.
These packs offer the same protective qualities and durability as conventional blister packs while contributing to a more circular and environmentally responsible packaging solution.
Practical Example
By incorporating sugarcane-derived polyethylene, Astellas Pharma reduces the environmental impact of its blister packaging, moving towards a more sustainable and carbon-neutral solution.
Astellas introduced the bio-blister packaging for the Irribow® Tablet (generic name: ramosetron hydrochloride) in Japan in FY2021 and plans to expand its use to other products, supporting their ongoing commitment to sustainability.
Benefits of Sustainable Blister Packaging
Sustainable blister packaging offers a wide range of environmental, economic, and consumer-related benefits.
Here are the key benefits of sustainable blister packaging.
1. Environmental Benefits
Reduced Waste: Sustainable materials reduce the amount of non-recyclable waste sent to landfills and oceans.
Lower Carbon Emissions: Eco-friendly production methods and the use of renewable materials helps to reduce greenhouse gas emissions.
Enhanced Biodegradability: Materials like PLA and paper break down more easily in the environment, reducing long-term pollution.
2. Economic Benefits
Cost Savings in Waste Management: Reduced environmental impact can lead to lower disposal and recycling costs.
Increased Consumer Demand: Consumers are increasingly supporting brands that demonstrate sustainability, which can boost sales and brand image.
Regulatory Compliance: By adopting sustainable practices, companies can stay ahead of the compliance curve as governments continue to implement stricter regulations.
3. Brand and Marketing Benefits
Enhanced Brand Image: Eco-friendly packaging can improve a brand’s reputation and appeal, particularly among environmentally conscious consumers.
Market Differentiation: It is easy for brands to recognize quickly in highly competitive markets.
Positive Public Relations: Implementing green practices can generate favorable media coverage and strengthen relationships with stakeholders.
By switching to materials that are recyclable, biodegradable, or derived from renewable resources, industries can make a positive impact on the planet while continuing to deliver high-quality, safe, and accessible products.
Challenges of Sustainable Blister Packaging
In sustainable blister packaging, there are a few challenges and limitations that companies must consider before moving into more eco-friendly solutions.
1. Material Performance and Protection
Barrier Properties: Some sustainable materials, like certain bioplastics or paper-based materials, may not be sufficient to provide the same level of barrier protection as traditional materials such as PVC or aluminum foil.
Products, especially those that are sensitive to moisture, light, or air, might not be adequately protected with eco-friendly materials.
This is the main concern for the pharmaceutical industry, where maintaining drug potency is very important.
Durability and Strength: Materials like r-PET, r-PP, r-HDPE and some bioplastics might not have the same level of strength and other qualities as compared to traditional PVC blister packs.
2. Higher Initial Costs
Material Costs: Sustainable materials always come with higher production costs compared to traditional plastics like PVC.
The higher cost of eco-friendly materials can increase the cost of the final product, which may make it difficult for businesses to remain in competitive markets.
Production Adjustments: Adopting sustainable materials and techniques requires training and production line modifications. This initial investment can be a major issue for companies that are already set up with traditional systems.
3. Infrastructure and Market Adoption
Recycling Challenges: Though sustainable materials like r-PET and r-HDPE are easy to recycle as compared to PVC, proper infrastructures are not established in certain regions. As a result, businesses sometimes may face logistic and supply issues during peak times.
Consumer Acceptance: Some consumers may be hesitant to adopt products with sustainable packaging, especially if there are concerns about performance and aesthetic look.
Future Trends in Blister Packaging
As the demand for more eco-friendly packaging grows, technological advancements are playing a key role in making sustainable blister packaging more efficient and affordable.
Here are some of the major technological advancements that are shaping the future of sustainable blister packaging.
1. Advanced Materials Development
Biodegradable and Compostable Materials: Advancements in bioplastics, such as PLA (Polylactic Acid), PHA (Polyhydroxyalkanoates), and PBS (Polybutylene Succinate), are making biodegradable and compostable blister packaging more viable.
These materials break down naturally without leaving behind waste.
2. Enhanced Recycling Technologies
Advanced Sorting and Recycling Systems: Improved sorting technologies, such as optical sorting and artificial intelligence (AI)-driven systems, are making it easier to separate and process mixed-material blister packs.
This increases the efficiency of recycling and reduces the contamination of recyclables, ensuring that more packaging is reused or repurposed.
Chemical Recycling: Chemical recycling is an emerging technology that allows plastics, including PVC, that are traditionally difficult to recycle, to be broken down and converted into basic monomers.
Additionally, because the material is converted back into its basic monomer form, it can be reused to produce high-quality materials, similar to virgin materials, ensuring the same performance and durability in new products.
3. Eco-Friendly Printing and Decoration Technologies
Sustainable Inks and Printing Techniques: Algae-based inks reduce the harmful environmental impact of traditional ink formulations, which often contain volatile organic compounds (VOCs).
These eco-friendly inks are now being used for printing on blister packaging, reducing the overall toxicity of packaging waste.

Digital Printing: Unlike traditional printing methods, digital printing eliminates the need for plastic-based printing plates, allowing on demand printing without set-up time and print wastages.
This reduces material waste and minimizes the disposal of excess ink once the operation is complete.
As technology continues to evolve, we can expect even more innovations in reducing packaging waste, improving recyclability, and lowering the environmental impact of blister packaging.
Conclusion
Sustainable blister packaging in the pharmaceutical industry is necessary to protect not only the product but also for planet and people, since traditional blister packs, like PVC blister packs, have significant environmental impacts.
By using bioplastics, paper materials, recycled materials, and sustainable techniques, manufacturers can reduce waste and lower their carbon footprint.
By adopting sustainable practices, manufacturers contribute to a cleaner, safer, and more responsible future. Supporting sustainable blister packaging is crucial for a healthier planet for future generations.
If there’s any important topic I missed, feel free to share your thoughts in the comments!
