Edible Water Pods are a groundbreaking, eco-friendly alternative to traditional plastic bottles. These small, jelly-like spheres encapsulate water within a thin, edible membrane, allowing people to quench their thirst without the need for plastic packaging.
The outer layer of each pod is made from natural, biodegradable materials—typically derived from seaweed and other plant-based sources—making it safe for consumption and gentle on the environment.
Introduction
The design of Edible Water Pods is as clever as it is simple. The membrane holds water securely, preventing leaks or spills, yet it’s soft enough to be easily bitten or dissolved.
Once consumed, there’s no waste left behind, eliminating the plastic bottle entirely.
This feature makes Edible Water Pods an excellent solution to one of our biggest environmental issues: plastic waste.
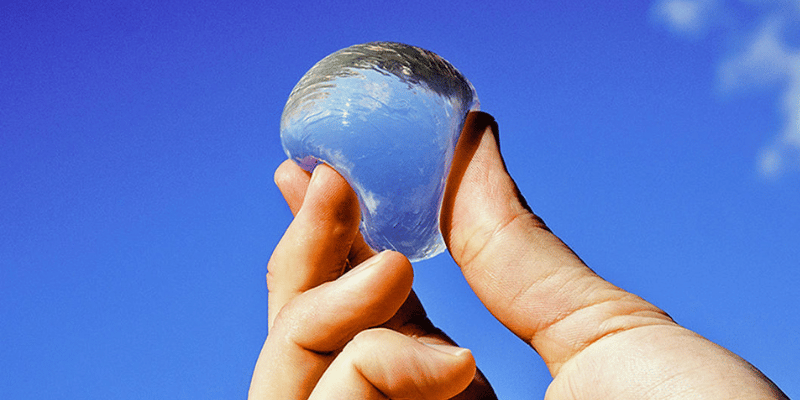

By choosing these pods over single-use plastic bottles, consumers can help to reduce plastic pollution and protect the planet.
Innovative and effective, Edible Water Pods provide an engaging way for environmentally conscious people to stay hydrated.
They bring together convenience and sustainability, making it easier for people to embrace eco-friendly choices in their everyday lives.
Environmental Impact
The environmental impact of Edible Water Pods is profound, especially when considering the immense plastic waste generated by single-use plastic bottles.
Each year, billions of plastic bottles are produced, used once, and discarded, contributing significantly to the world’s mounting plastic pollution crisis.
In 2022 alone, it was estimated that more than 500 billion plastic bottles were used globally.
Shockingly, less than 10% of these bottles are effectively recycled, meaning most of them end up in landfills or the ocean, where they can take hundreds of years to degrade.
Single-use plastic bottles are particularly harmful to the environment because they’re designed for short-term convenience yet leave a long-term footprint.
When discarded, these bottles break down into microplastics, which enter soil, rivers, and oceans, affecting marine life and eventually finding their way into the food chain.
Studies show that plastic pollution now affects over 700 marine species, many of which ingest or become entangled in plastic debris, often leading to fatal outcomes.
This pollution has become so extensive that it’s predicted there will be more plastic than fish in the ocean by 2050.

Edible Water Pods provide a sustainable alternative to this plastic bottle. Unlike plastic bottles, the pods’ biodegradable membrane breaks down naturally without leaving behind toxic residue.
This solution is especially significant for public events, festivals, and sports gatherings, where single-use bottles are prevalent.
By replacing plastic bottles with Edible Water Pods at such venues, we can drastically cut down on waste and reduce the environmental strain caused by single-use plastics.
How to Make Edible Water Pods?
Edible Water Pods are crafted using a simple yet innovative process that centers on eco-friendly materials, primarily derived from natural sources like seaweed.
The outer membrane that holds the water is typically made from sodium alginate, a gelatinous substance extracted from brown seaweed, and calcium chloride.
Sodium alginate is widely used in food and pharmaceutical products, known for its natural, non-toxic, and biodegradable properties.
These materials are chosen not only for their sustainability but also for their ability to create a stable yet edible outer layer that securely holds water without any plastic casing.
The process of creating Edible Water Pods begins with a method called spherification, which involves dipping a liquid-filled sphere into a bath of calcium chloride.
When sodium alginate in the water reacts with calcium ions from the bath, it forms a gel-like membrane around the water, creating a small, self-contained pod.
This membrane is thick enough to keep the water intact but thin enough to be easily bitten or dissolved, making it perfect for single servings.
The process is incredibly efficient and can be scaled up to produce large numbers of pods quickly.
Once formed, Edible Water Pods are ready for consumption. They’re simple to use—people can pop the pod into their mouths and bite into the thin membrane to release the water inside, consuming both the water and the outer layer.
For those who prefer not to eat the membrane, it can also be discarded as it biodegrades quickly without harming the environment.
The design also allows for easy flavor infusion, meaning the pods can contain flavored water or even electrolyte solutions, adding variety and enhancing hydration options.
This innovative approach to packaging is a major shift from traditional plastic bottles, offering a plastic-free, biodegradable, and natural alternative that is as functional as it is environmentally friendly.
Benefits of Edible Water Pods
Edible Water Pods offer several compelling benefits over traditional plastic bottles, especially in terms of environmental sustainability and reducing our reliance on single-use plastics.
Unlike plastic bottles, which are often made from petroleum-based materials that take hundreds of years to degrade, Edible Water Pods are eco-friendly and biodegradable.
The outer membrane of these pods is made from natural, plant-based materials, often derived from seaweed, meaning they break down quickly and safely in the environment without leaving harmful residues.
This allows them to provide a truly waste-free solution for hydration and cutting down huge plastic pollution.
One of the key advantages of Edible Water Pods is their ability to reduce the carbon footprint associated with the production and recycling of plastic bottles.
Manufacturing plastic bottles is energy-intensive, relying on fossil fuels, which contribute to greenhouse gas emissions.
Additionally, the recycling process for plastics, while beneficial, still requires significant energy and resources and is only partially effective, as many bottles never make it through the recycling chain.
In contrast, the materials and process involved in creating Edible Water Pods are far less resource-intensive, resulting in a much lower carbon footprint.
Beyond production, Edible Water Pods also eliminate the need for transporting bulky bottles, further reducing their environmental impact.
Plastic bottles are often shipped long distances, contributing to emissions from transportation. In contrast, Edible Water Pods are compact, lightweight, and can be produced locally for specific events, festivals, or urban sectors, minimizing the need for long-distance transportation.
By choosing Edible Water Pods over plastic bottles, consumers are supporting a more sustainable lifestyle, one that aligns with reducing plastic waste and promoting biodegradable alternatives.
Challenges of Edible Water Pods
While Edible Water Pods present an exciting, sustainable alternative to plastic bottles, they come with their own set of challenges and limitations that impact their widespread adoption.
Storage and Shelf Life
One of the primary limitations is the storage and shelf life of Edible Water Pods.
Unlike plastic bottles, which can hold liquids for long periods, Edible Water Pods are much more perishable.
The natural membrane that makes them biodegradable also makes them less durable, meaning they can’t be stored for extended periods or in conditions that might compromise the integrity of the outer layer.
For instance, extreme temperatures, humidity, or rough handling can weaken the membrane, causing leaks or bursts.
Distribution Challenges
Distributing Edible Water Pods on a large scale presents another challenge. Plastic bottles are robust, stackable, and easy to transport, making them ideal for large-scale distribution and convenient storage in retail outlets.
Edible Water Pods, however, are fragile and need careful handling to avoid rupture, which complicates transportation logistics.
Cost Considerations
Another limitation is the cost associated with producing Edible Water Pods. Currently, they are more expensive to manufacture than standard plastic bottles.
While this is partly because they are still an emerging product, their reliance on sustainable, natural materials like seaweed and the specialized spherification process used to create the membrane contribute to higher production costs.
This can make them less affordable for consumers, especially in comparison to low-cost, mass-produced plastic bottles.
Consumer Adoption and Familiarity
Another hurdle to the success of Edible Water Pods is consumer awareness and acceptance.
For many people, drinking water from a pod rather than a bottle is an unfamiliar experience.
The idea of consuming the outer layer along with the water may feel strange or unappealing to some.
Need for Awareness and Education
To ensure Edible Water Pods become a viable alternative, consumer awareness and education are essential.
People need to understand how the pods work, the environmental benefits they offer, and why they’re a sustainable choice over single-use plastics.
In addition, introducing them at public events, festivals, and eco-friendly initiatives can help familiarize people with the product and normalize its use.
This kind of awareness campaign can go a long way in encouraging consumers to make the switch and support a more sustainable product.
Current Applications and Brands of Edible Water Pods
Edible water pods have emerged as a sustainable alternative to single-use plastic bottles, with several companies pioneering their development and application.
Notpla and Ooho
Notpla, a London-based startup, has been at the forefront of this innovation with their product, Ooho. Founded by Pierre Paslier and Rodrigo Garcia Gonzalez, Notpla aims to create packaging solutions that naturally biodegrade, reducing environmental impact. Ooho is an edible, biodegradable membrane made from seaweed and plants, designed to encapsulate water and other liquids. The membrane is tasteless and can be consumed along with the liquid or discarded, as it biodegrades in approximately six weeks.
Applications in Public Events
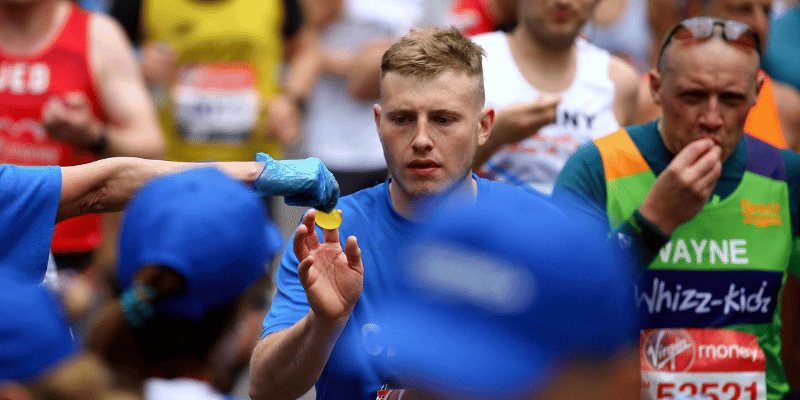

Ooho has been trialed in various public places to reduce plastic waste. Notably, during the 2019 London Marathon, over 30,000 Ooho capsules filled with Lucozade Sport were distributed to runners at Mile 23, replacing traditional plastic bottles and cups. This initiative aimed to cut down on the 920,000 plastic bottles used in the previous year’s marathon.
Beyond marathons, Ooho has been utilized at music festivals, sporting events, and private functions in cities like London, San Francisco, and Boston. These trials demonstrate the feasibility of using edible water pods in large-scale events, offering a practical solution to single-use plastic waste.
Collaborations and Product Expansion
Notpla has collaborated with various organizations to expand the use of their edible packaging. In partnership with Just Eat, they developed seaweed-lined takeaway containers, providing a sustainable alternative to traditional plastic-lined boxes. This collaboration highlights the versatility of Notpla’s materials in different applications.
Additionally, Notpla has explored the use of their edible pods for energy gels in sporting events, offering athletes a sustainable option for on-the-go nutrition. These developments showcase the potential of edible packaging to replace plastic in various sectors.
Global Recognition and Future Prospects
Notpla’s innovative approach has garnered international attention. In 2022, they were awarded the Earthshot Prize for their efforts in creating waste-free packaging solutions. This recognition underscores the global relevance of their work in addressing plastic pollution.
The successful trials and collaborations indicate a growing acceptance of edible water pods as a viable alternative to plastic bottles. As awareness of plastic pollution increases, the adoption of such sustainable solutions is likely to expand, potentially transforming packaging practices across industries.
Future Potential and Innovations in Edible Water Pods
The future of edible pods goes beyond just water, offering exciting possibilities for sustainable packaging across many industries. This innovative technology has the potential to transform how we package liquids and even certain foods, providing an eco-friendly solution for single-use plastics.
Expanding Beyond Water
Edible pods could be adapted to hold other beverages like juice, sports drinks, or even coffee, providing a convenient, waste-free way for people to enjoy these drinks on the go.
For example, at marathons or sports events, these pods could replace the small plastic bottles and cups often used to distribute beverages to participants, reducing plastic waste in these sectors.
Edible pods could also be used for single-serve condiments like ketchup, mustard, or salad dressing.
Imagine receiving a small, edible pod of ketchup with your meal instead of a plastic packet—once the ketchup is used, there’s no leftover waste to dispose of.
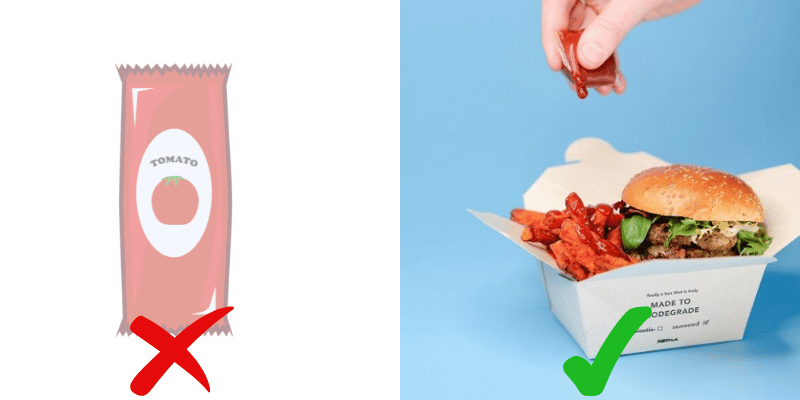
Innovations in Food Packaging
In addition to liquids, edible pods could be used to encase small snacks or supplements, like single servings of nuts, vitamins, or even candy.
This would eliminate the need for individual plastic wrappers, which often end up as litter.
Since the edible membrane is safe to eat and biodegradable, it provides a simple solution for environmentally conscious consumers who want to reduce their plastic footprint.
Industry Potential
As the technology behind edible pods advances, it could play a role in several industries beyond food and beverages.
For example, it might replace plastic packaging in the cosmetics industry, holding small samples of creams or lotions in a way that’s both hygienic and environmentally friendly.
The pharmaceutical industry could also benefit, using edible pods to package single doses of medicines in an easy-to-consume form, reducing reliance on plastic PET bottles for cough syrup.
Future Innovations
To make this technology more accessible, scientists and developers are working on creating even stronger and more versatile membranes that can hold a broader range of liquids and resist damage during transport.
With improvements in production methods, edible pods could become more affordable, enabling them to reach larger markets and compete directly with traditional plastic packaging.
As demand for sustainable packaging grows, the development of edible pods is likely to expand, offering eco-friendly alternatives across multiple sectors.
By replacing single-use plastics with edible pods, we can reduce plastic waste significantly and move toward a future with less pollution and more sustainable consumption options.
With ongoing research and innovation, edible pods hold the potential to reshape how we package and consume products, paving the way for a cleaner and greener world.
Consumer Perspective
From a consumer’s perspective, edible water pods offer a unique experience that blends sustainability with convenience, though they may require a bit of an adjustment for users accustomed to traditional plastic bottles.
Taste and Texture
One of the primary aspects of edible water pods that consumers notice is the taste and texture of the membrane.
Since the membrane is usually made from seaweed extract, it’s tasteless and odorless, meaning it won’t interfere with the flavor of the water inside.
However, for first-time users, the texture of the outer layer can feel unusual—similar to a soft, jelly-like material.
Some consumers find it fun and novel, while others may need time to get used to biting into the pod rather than sipping from a bottle.
In some cases, the membrane can also be flavored to enhance the user experience, adding an extra layer of appeal, especially in flavored water or juice pods.
Convenience and Portability
Edible water pods are incredibly convenient for on-the-go hydration, as they’re small, lightweight, and don’t require a cap or bottle.
This can be especially handy at events like marathons or festivals, where carrying a bulky plastic bottle isn’t ideal.
For quick hydration, consumers can simply pop a pod into their mouths and discard the membrane if they choose not to eat it.
Since the membrane biodegrades quickly, it leaves no environmental footprint.
Sustainability and Eco-Friendly Appeal
For environmentally conscious consumers, the benefits of edible water pods are a major draw. Knowing that they are reducing plastic waste and contributing to a greener planet adds a sense of fulfillment to the user experience.
However, some consumers may initially hesitate due to unfamiliarity with the product or concerns over its durability and portability.
As awareness grows and more people experience the benefits, these hesitations are likely to decrease, encouraging more widespread acceptance of this eco-friendly option.
Social Experience and Novelty
Edible water pods bring a sense of novelty and social appeal. Consumers may find the experience of eating their water intriguing, and it can serve as a conversation starter in group settings.
For younger generations and eco-conscious consumers, trying a product like this is not only about hydration but also about making a statement on sustainability.
Conclusion
In conclusion, edible water pods represent an innovative and eco-friendly step forward in the fight against plastic waste. By providing a biodegradable, convenient, and engaging alternative to traditional plastic bottles, these pods align perfectly with the growing need for sustainable solutions.
While there are challenges to overcome, such as distribution and consumer adoption, the benefits they bring to both consumers and the environment are undeniable. As more people embrace this new way of hydrating, edible water pods have the potential to significantly reduce plastic pollution, paving the way for a cleaner, greener future.
Embracing innovations like edible water pods not only makes a positive impact on our planet but also encourages a shift toward more responsible and sustainable consumption habits for generations to come.
